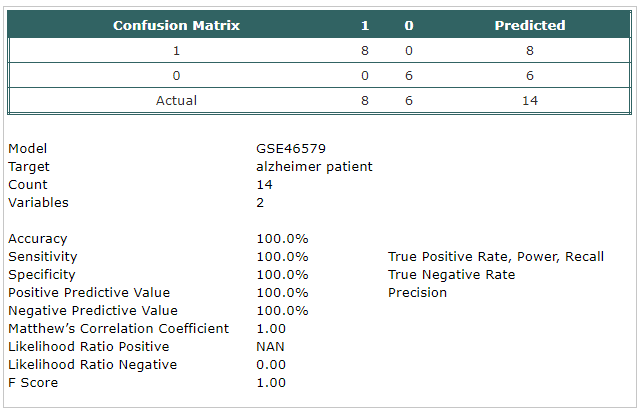
GSE46579
|
| What
We Learned |
- Alzheimer disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia but the identification of reliable, early
and non-invasive biomarkers remains a major challenge. This study presents a novel miRNA-based signature for detecting
AD from blood samples.
|
- 12-miRNA signature can differentiate between
AD and controls with an accuracy of 93%, a specificity of
95% and a sensitivity of 92%.
- The differentiation of AD from other neurological diseases
is possible with accuracies between 74% and 78%. The differentiation
of the other CNS disorders from controls yields even higher accuracies.
- Upregulated:
- brain-miR-112
- brain-miR-161
- hsa-let-7d-3p
- hsa-miR-5010-3p
- hsa-miR-26a-5p
- hsamiR-1285-5p
- hsa-miR-151a-3p
- Downregulated:
- hsa-miR-103a-3p
- hsa-miR-107
- hsa-miR-532-5p
- hsa-miR-26b-5p
- hsa-let-7f-5p
|
- As of today, final diagnosis of AD can only be achieved
by autopsy making the identification of reliable, early, and non-invasive biomarkers a major challenge.
|
- Finding such non-invasive, reliable diagnostic tools is of paramount
importance as it appears that early intervention in the prodromal stage of AD or the identification and therapy of
those patients with mild cognitive impairment who will transform to AD rapidly might be
a possibility to delay the onset of AD substantially.
|
- According to the S3 guidelines, an increased level
of tau protein together with a decreased level of beta
amyloid-1-42 provides strong evidence for the presence of AD.
|
- Furthermore, combinatorial analysis of
Aß levels and tau levels can discriminate between patients with stable mild
cognitive impairment (MCI) and patients with progressive MCI into AD or other types of dementia with a sufficient
diagnostic accuracy.
|
- Molecular genetics analyses of common single nucleotide
polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes such as presenilin or ApoE4 did not
significantly improve risk estimation for the susceptibility of AD.
- Likewise, there is no consistent evidence for an association between
AD and genetic variation of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
|
- There is increasing effort to develop molecular diagnostic
markers that meet requirements like easy accessibility, for example, from blood, sufficiently high specificity and
sensitivity, low costs and applicability by laboratories with standard equipment.
|
- Moreover, Tan et al. provided evidence that the proteins
p53 and p21 can be used to detect AD using blood samples.
- A receiver operating characteristic curve analysis
revealed a specificity of 76% and a sensitivity of 84% for p53, 88% and 82% for p53(ser15), 80% and 75%
for p21, and 84% and 68% for p21(thr145).
|
|
| What
We Did |
- A classification model has been built using Trainset.
The selected probes were:
- hsa-mir-148b>hsa-mir-148b-5p
- hsa-mir-144>hsa-mir-144-5p
|
- The model has been tested using Testset.
|
 |
|

