GSE76462
|
| What
We Learned |
- The identification of circulating microRNAs
(miRNAs) in the blood has been recently exploited for the development of minimally invasive tests for the early
detection of cancer. Nevertheless, the clinical transferability
of such tests is uncertain due to still-insufficient standardization and optimization of methods to detect circulating
miRNAs in the clinical setting.
|
- The major source of analytical variation came from
RNA isolation from serum, which could be corrected by use of external (spike-in) or
endogenous miRNAs as a reference for normalization.
|
- Increasing evidence has confirmed that miRNAs exist in almost every
biological fluid and that signatures of circulating miRNAs with diagnostic potential can be
identified for many diseases, including cancer. Therefore, circulating miRNAs have been proposed as
useful biomarkers to improve risk assessment, diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of therapy response.
|
- The variability introduced
in the RNA extraction step could be corrected by normalizing the amount of input RNA used in the
quantification.
- In the absence of any reliable methodology for quantification of RNA isolated from serum,
it is preferred to use fixed volumes of input RNA and exogenous (such as synthetic spiked-in miRNAs) or endogenous
(6 HK miRNAs) references for data normalization.
Although both strategies were effective, better results has
consistently been achieved by use of a combination of 6 endogenous
miRNAs.
|
- When the impact of preanalytical variables was systematically
analyzed, we found that the levels of circulating miRNAs were often heavily influenced. One major
confounding variable was the nutritional status of individuals
at phlebotomy.
- Similarly, serum contamination by hemolysis caused a marked variability in miRNA level.
|
- Use strictly controlled procedures in the way samples are collected
and prepared.
|
- A bias has been observed in the yields of extracted
miRNA between different runs performed on the same day. This systematic bias was
effectively corrected by normalization and did not alter miR-Test performance.
|
|
| What
We Did |
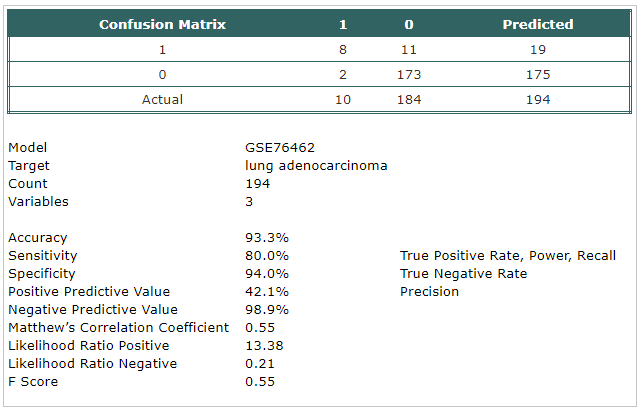
- A classification model has been built using Trainset.
The selected probes were:
- hsa-mir-140-5p
- hsa-mir-92a
- hsa-mir-331-3p
|
- The model has been tested using Testset.
|
 |
|

