GSE90828
|
| What
We Learned |
- Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is an intermediate state between normal aging and dementia including Alzheimer's disease.
CONCLUSION:
Differential correlation analysis, a bioinformatics tool to elucidate complicated and interdependent biological systems behind diseases, detects effective MCI markers that cannot be found by single molecule analysis such as t-test.
|
- Early detection of dementia, and MCI, is a crucial issue in terms of secondary prevention. Blood biomarker detection is a possible way for early detection of MCI.
|
- Differential correlation analysis, which detects difference on correlation of two variables in case/control study, was carried out to
plasma microRNA (miRNA) expression profiles of 30 age- and race-matched controls and 23 Japanese MCI patients.
|
- The 20 pairs of miRNAs, which consist of 20 miRNAs, were selected as MCI markers. Two pairs of miRNAs
(hsa-miR-191 and hsa-miR-101, and hsa-miR-103 and
hsa-miR-222) out of 20 attained the highest area under the curve
(AUC) value of 0.962 for MCI detection.
|
- Other two miRNA pairs that include hsa-miR-191 and
hsa-miR-125b also attained high AUC value of ≥ 0.95.
|
- Pathway analysis was performed to the MCI markers for further understanding of biological implications. As a result, collapsed correlation on
hsa-miR-191 and emerged correlation on hsa-miR-125b might have key role in MCI and dementia
progression.
|
|
| What
We Did |
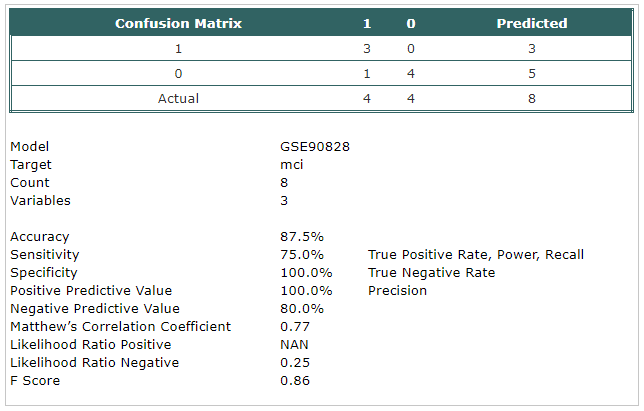
- A classification model has been built using Trainset.
The selected probes were:
- hsa-mir-339-3p
- hsa-mir-365
- hsa-mir-187
|
- The model has been tested using Testset.
|
 |
|

